What is Salvage Value, and How to Calculate After-Tax Salvage Value?

The choice of depreciation method can significantly influence the financial portrayal of an asset’s value over time. For instance, using the straight-line method, the asset’s cost is evenly distributed over its useful life, resulting in a consistent depreciation expense each period. In contrast, the declining balance method accelerates depreciation, offering larger expense deductions in the earlier years. The salvage value guides not only the total depreciation expense but also its distribution across financial periods, impacting the asset’s book value and the company’s financial statements.
Can straight-line depreciation be used for tax purposes?
Underestimating the salvage value can result in a higher depreciation expense, which can reduce the asset’s net book value and understate the company’s financial position. Units of production method – This method involves depreciating the asset based on how much it is used. The advantage of this method is that it accurately reflects the actual use of the asset. However, it can be difficult to estimate how much the asset will be used over its useful life. Declining balance method – This method involves depreciating the asset by a fixed percentage each year.
- On the income statement, the depreciation expense, influenced by the salvage value, affects the net income.
- This formula is best for companies with assets that lose greater value in the early years and that want larger depreciation deductions sooner.
- For example, a person leasing only one passenger automobile during a tax year is not regularly engaged in the business of leasing automobiles.
- ABC Manufacturing Company purchased a specialised machine for $50,000, with an estimated useful life of 10 years.
- Usually financial statements refer to the balance sheet, income statement, statement of comprehensive income, statement of cash flows, and statement of stockholders’ equity.
How to Calculate Salvage Value
For example, if an asset has a purchase price of $10,000 and a salvage value of $2,000, the depreciated cost of the asset would be $8,000. However, if the salvage value of the asset was $4,000, the depreciated cost would be reduced to $6,000. It is important to consider the salvage value of an asset when calculating the cost of ownership, as it can have a significant impact on the overall cost. To accurately estimate salvage value, companies should consider several factors, including the age and condition of the asset, market HOA Accounting trends, and technological advancements. It is also important to consider the specific industry and the asset’s intended use. For instance, a computer’s salvage value will be significantly lower than that of a manufacturing machine because technology advances much more quickly in the computer industry.
Debt Refinancing: Principles, Types, and Financial Impacts
Cost of Goods Sold is a general ledger account under the perpetual inventory system. The book value of an asset is the amount of cost in its asset account less the accumulated depreciation applicable to the asset. The book value of an asset is also referred to as the carrying value of the asset.

Double-Declining Balance Depreciation Method
- You can revise future depreciation calculations to reflect the updated salvage value.
- The book value of a company is the amount of owner’s or stockholders’ equity.
- The class for your property was determined when you began to depreciate it.
- Market conditions play a significant role in determining an asset’s salvage value.
- Calculating salvage value is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of various factors.
The method can help you predict your expenses and determine when it’s time for a new investment and prepare for tax season. Learn how to calculate straight-line depreciation, when to use it, and what it looks like in the real world. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31. The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position. The amounts spent to acquire, expand, or improve assets are referred to as capital expenditures.


Accurate estimation of salvage value can aid in forecasting cash flows and anticipating future proceeds, though it’s typically an estimate rather than a precise figure. Utilizing methods such as the percentage of cost, appraisals, or historical comparables helps companies make informed depreciation and financial planning decisions. This method depreciates the machine at its straight-line depreciation percentage times its remaining depreciable amount each year. In earlier years, an asset’s higher value leads to larger depreciation expenses, which decrease annually. You can change from the declining balance method to the straight line method at any time during the useful life of your property without IRS consent. However, if you have a written agreement with the IRS that prohibits a change, you must first get IRS permission.
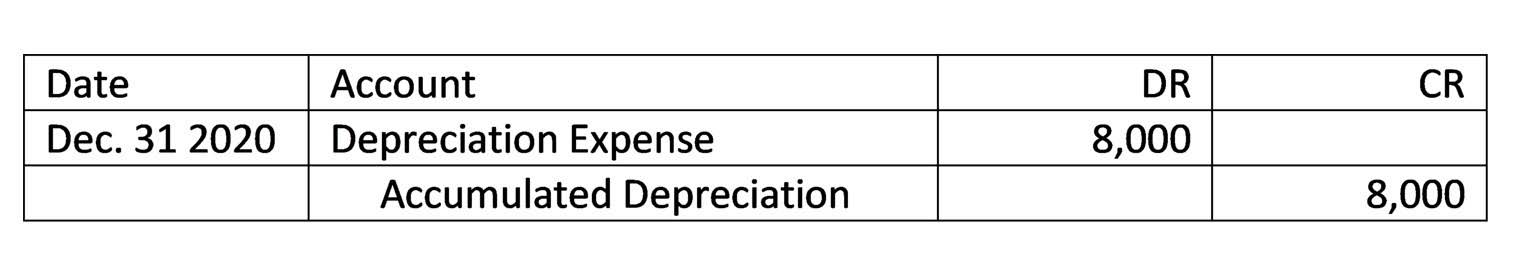
If you used the percentages above, you cannot claim depreciation for this property after 1995. 3-year property includes automobiles, light-duty trucks (actual unloaded weight less than 13,000 pounds), and tractor units for use depreciation salvage value over-the-road. Any other horses over 12 years old when you placed them in service are also included in the 3-year property class. Here useful life in the form of unit produced is the total unit produced in the year divided by total expected units to be produced. The beginning of period (BoP) book value of the PP&E for Year 1 is linked to our purchase cost cell, i.e.
- Therefore, it would be helpful if you would include your daytime phone number, including the area code, in your correspondence.
- However, the depreciation will stop when the asset’s book value is equal to the estimated salvage value.
- The annual depreciation can be calculated by subtracting the residual value from the PP&E purchase price and dividing that amount by the useful life assumption.
- Factors such as wear and tear, market conditions, and technological advancements can all impact the value of an asset.
- Businesses must stay informed about tax laws and regulations to optimize their tax positions and ensure compliance.
- It’s the value for which the asset can be sold or disposed of after it has served its purpose.
According to IAS 16, the value of equipment or machinery after its useful https://ecoenergy.vn/fifo-vs-lifo-inventory-valuation/ life is often termed the scrap value. Understanding salvage value helps in budgeting and long-term financial planning by ensuring accurate depreciation calculations. Therefore, the DDB depreciation calculation for an asset with a 10-year useful life will have a DDB depreciation rate of 20%.

At the end of three years the truck’s book value will be $40,000 ($70,000 minus $30,000). So using the example above, the cost was 10,000, salvage value 1,000 and useful life 3 years. So, the estimated salvage value of the computer after 5 years is $300, which was the same as the initial estimated salvage value.